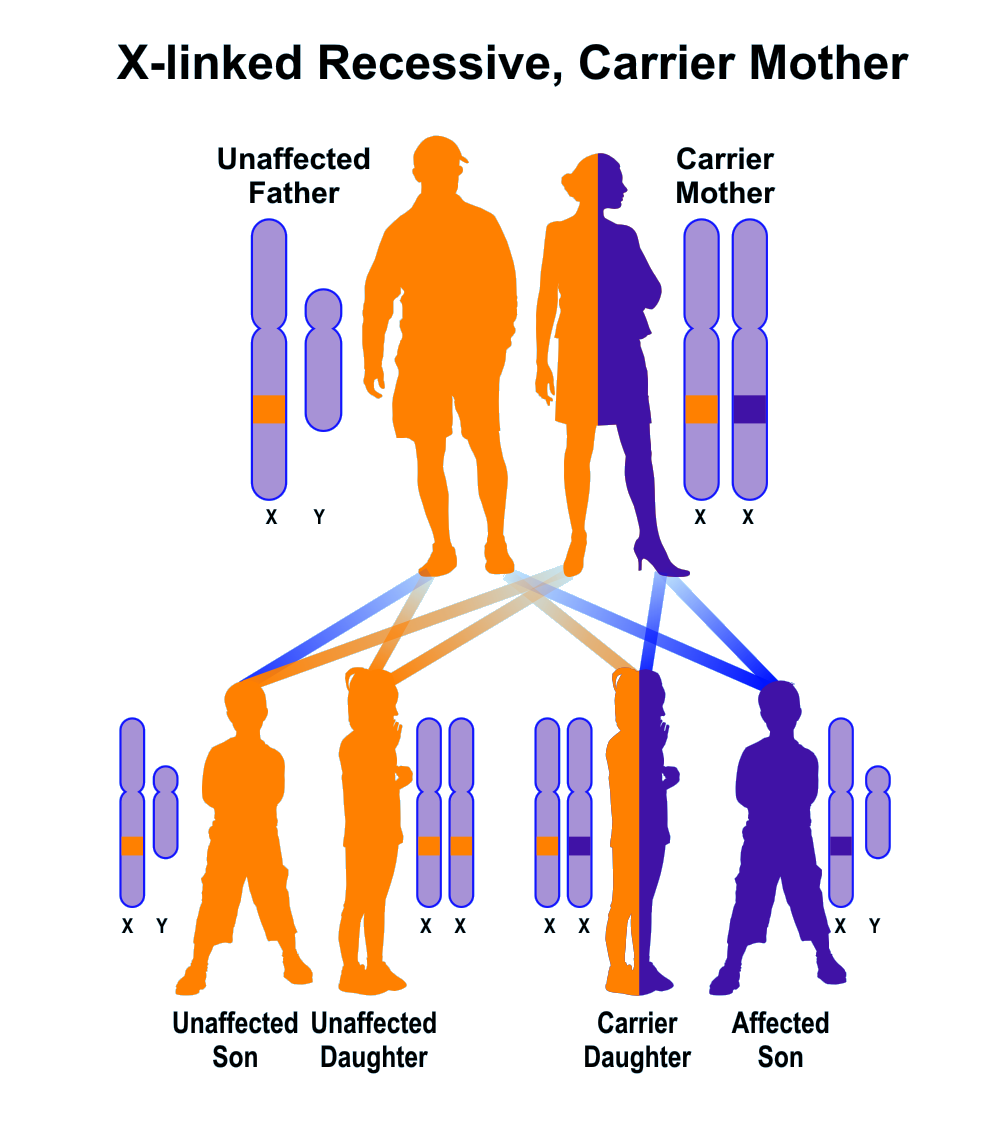
X-linked disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and both sexes can pass this to their children. If the mutation is in a recessive gene and carried by the mother, she usually does not have the disease since the normal X chromosome without the mutation neutralizes the mutation in the abnormal X chromosome. However, half her sons will inherit the mutation-containing X chromosome and therefore have the X-linked disease. Half the daughters will inherit the mutation-bearing X chromosome and are usuallly healthy 'carriers'.