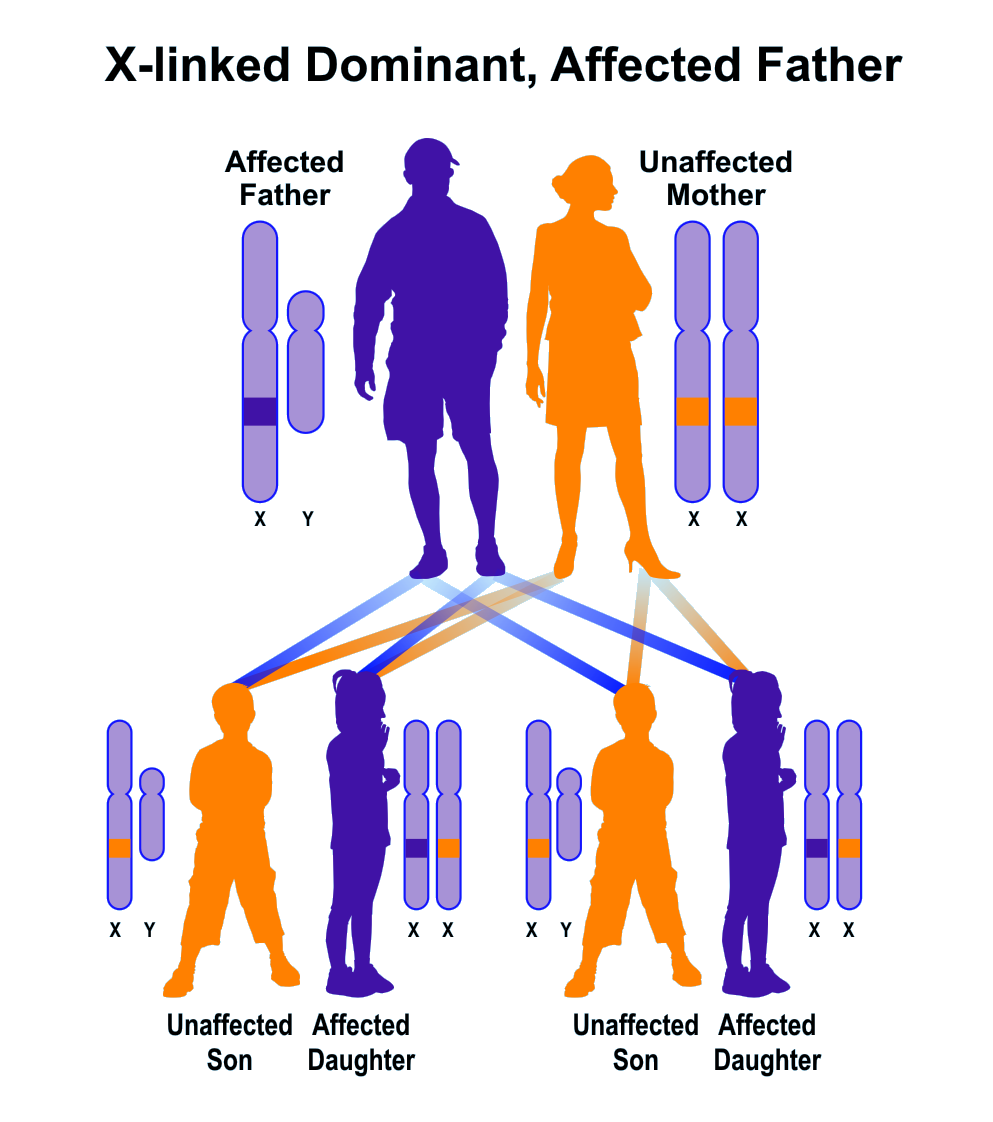
X-linked inheritance patterns result when disease-causing mutations are located on the X chromosome. Males have one X chromosome while females have two. A mutation on the male's X chromosome frequently is lethal or renders him unable to reproduce. However, in rare cases when males have children, they can expect that all of then will inherit the condition.